Conducting Music
Aleatoric music is a form of composition in which a significant element is left to the determination of its performers. Terry Riley’s “In C” is a composition of 53 phrases to be played in sequence, but each performer individually determines the number of times they play each phrase. They form a collective conductor yet also act as many conductors as the role is distributed among each of them.
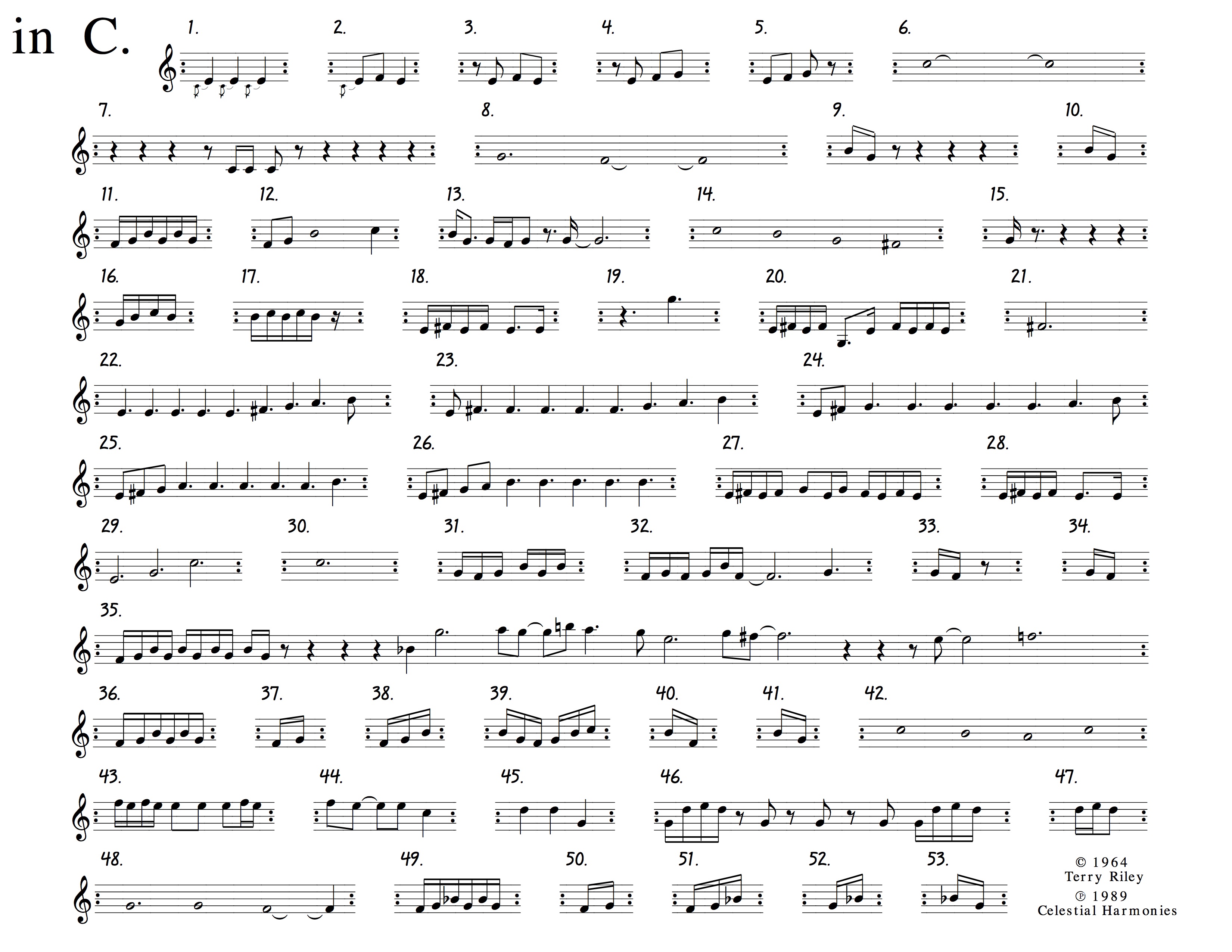

Bird Sounds in C proposes to create an orchestra of birds to play “In C”. For each bird, the phrases of “In C” are recomposed by alternating and arranging an individual “C note” extracted from their bird song. These phrases are then further composed by a single user who chooses when to advances each bird through the composition.
Constructing Sounds
Rather than starting with notation and then playing the written composition as a “live” performance, Bird Sounds in C instead starts with recorded sounds and reorders extracted elements to form the phrases of Riley’s “In C”. By using recorded bird songs—sounds with specific structure and meaning within their species—and recomposing them into a new composition, the sounds are given new meaning and recontextualized outside of “wildlife”.
The written score for “In C” appears monophonic, consisting of a single melody without chords or harmonies. However, through Riley’s intended method of performance, the various phrases and patterns overlap to create a densely layered and heterophonic texture.1
Reinterpreting this dense texturing, Birds in C instead uses the complex polyphonic sounds of bird songs. When visualized as sonograms, the layered frequencies of recorded bird songs are striking. 2
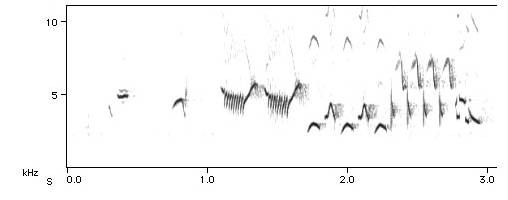
Using the sonogram as a visual artifact of the bird song, I identified a snippet which approximated “C” which I then transposed and arranged into Riley’s phrases. In this way, the translation of recorded sound to extracted and reordered elements attempts to use polyphonic sounds as monophonic approximations of single notes.
Bird Sounds Iteration-01
Click the circle to start and advance the bird sounds
Midi Sounds Iteration-01
Prior to working with bird sounds, I used midi to create the tones. One user controlled two “musicians” to advance through the piece using the keyboard. When purely using midi, the resulting audio was to distinguish into two “musicians”.
Questions of Playability
- What is the allowable degree of asynchronization?
- Does the computational aspect create a system which removes human variability (i.e. the code makes sure when a phrase is advanced, it comes in on the first beat of a bar – or does the musician need to keep track of this?
- How much content from the original notation of the piece does the user need to know? What visual indicates are needed to make choices about when to advance one bird or another?